Understanding Tardive Dyskinesia: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Understanding the complexities of Tardive Dyskinesia can be crucial for your health journey, and as you browse options to manage its symptoms, you'll discover valuable insights and treatment pathways that could transform your quality of life.

What is Tardive Dyskinesia?
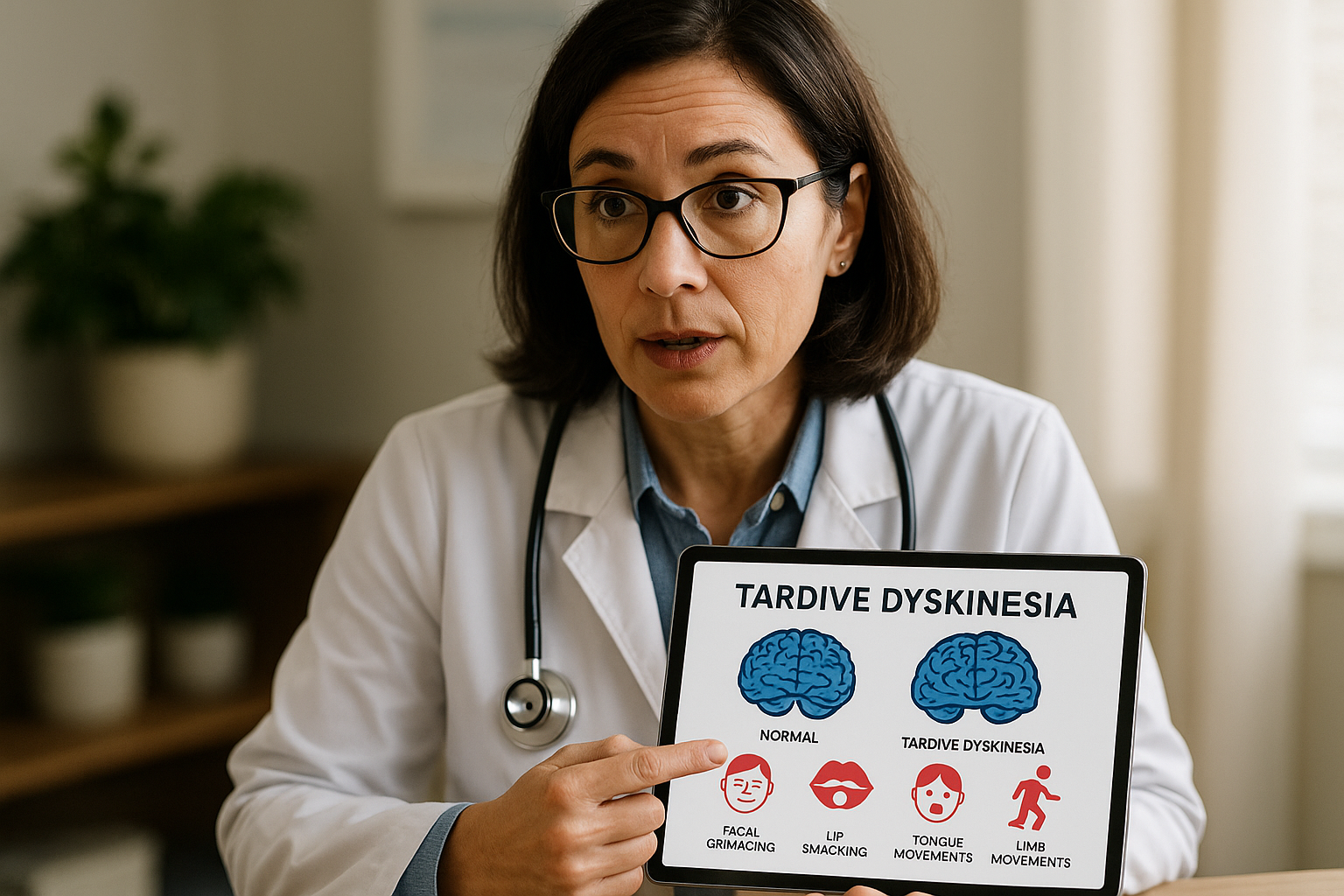
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary, repetitive body movements, often affecting the face, tongue, and limbs. This condition is typically a side effect of long-term use of antipsychotic medications, which are often prescribed for psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. The movements can be subtle, such as mild lip smacking or blinking, or more pronounced, involving significant movement of the arms and legs.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of Tardive Dyskinesia can vary widely among individuals, making it a challenging condition to diagnose. Common symptoms include grimacing, tongue movements, lip smacking, puckering, and rapid eye blinking. In some cases, individuals may experience movements of the fingers, arms, or legs. Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for effective management and treatment.
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing Tardive Dyskinesia involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically a neurologist or psychiatrist. The process includes a detailed medical history review, focusing on medication use, and a physical examination to assess the presence and severity of involuntary movements. Healthcare providers may use specific scales, such as the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS), to quantify the severity of the symptoms1.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Tardive Dyskinesia, several treatment options can help manage its symptoms:
- Medication Adjustments: Reducing or discontinuing the use of the causative antipsychotic medication can sometimes alleviate symptoms. However, this must be done under medical supervision to avoid exacerbating underlying psychiatric conditions.
- Medications for TD: FDA-approved drugs such as valbenazine (Ingrezza) and deutetrabenazine (Austedo) have shown efficacy in reducing symptoms of TD2.
- Botulinum Toxin Injections: In some cases, botulinum toxin (Botox) injections can be used to temporarily paralyze affected muscles, reducing involuntary movements.
- Supportive Therapies: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help individuals improve their quality of life by teaching them strategies to cope with and manage symptoms.
Financial Considerations and Support
Managing Tardive Dyskinesia can be costly, especially with the need for ongoing medication and therapy. It's important to explore insurance options, patient assistance programs, and generic medication alternatives to reduce costs. Some pharmaceutical companies offer financial assistance programs for medications like Ingrezza and Austedo, making them more accessible to those in need3.
Living with Tardive Dyskinesia
Living with Tardive Dyskinesia requires a comprehensive approach involving medical management, lifestyle adjustments, and support networks. Engaging with support groups and online communities can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the challenges of living with TD. Additionally, staying informed about new treatment options and research developments can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care.
By understanding Tardive Dyskinesia and actively exploring treatment options, you can take control of your health journey and improve your quality of life. For those interested in learning more, specialized resources and expert consultations are available to guide you through managing this condition effectively.